Autosomal dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Review
Abstract
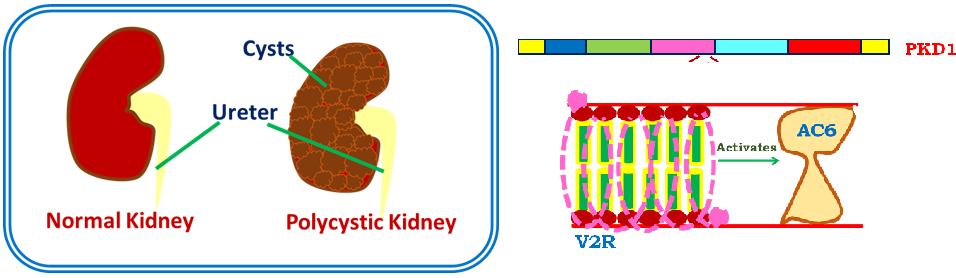
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is an inherited renal disease, characterized by gradual growth of multiple renal cysts, hypertension and end stage renal disease (ESRD). ADPKD shows progression with age where complications due to hypertension are more significant. Genetic testing and imaging have been found essential for the diagnosis, follow-up and detection of complications in patients. Genetic analysis revealed that mutation in two genes named as PKD1 and PKD2 is responsible for ADPKD. Several drugs like Tolvaptan, Triptolide, Somatostatin analogs etc. presently under clinical trials, have been found to show promising results. To date, there is no approved therapy for the permanent cure of ADPKD. Still, advancement in the technology and the understanding of the biological aspects of this disease has generated a spark to investigate new potential therapies to minimize the morbidity and mortality of the disease. The genetic testing and imaging, genetic analysis progeny of disease, possible drug candidates and recent advances in ADPKD management have been reviewed here.
Keywords
autosomal; dominant; polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD); renal disease (ESRD); PKD1; PKD2; PC1; PC2
Full Text:
PDFRefbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
ISSN: 2394-2274Â Journal of Biomedical and Therapeutic Sciences - International journal for Biomedical Research and Clinical studies advances
 ISSN: 2394-2274
ISSN: 2394-2274