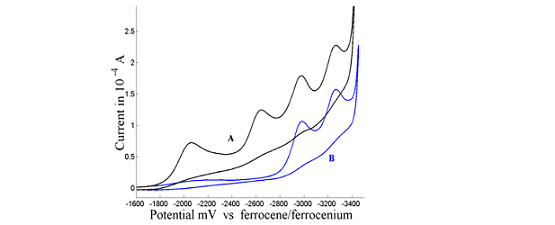
Electrochemical reductive cleavage of carbon-halogen bonds – application of Marcus theory in the analysis of nonlinear activation-driving force relationships
Abstract
Keywords
References
J.M. Saveant. Electron transfer, bond breaking and bond fragmentation. Adv. Phy. Org. Chem. 2000, 35, 117-192.
J.M. Saveant. A simple model for the kinetics of dissociative electron transfer in polar solvents. Applications to the homogenous and heterogeneous reduction of alkyl halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 6778-6795.
L. Eberson. Kolbe electrolytic synthesis IV. Theoretical investigations of the mechanism by standard potential calculations. Acta Chem. Scand. 1963, 17, 2004-2018.
M.T.C. Koper. Combining experiment and theory for understanding electrocatalysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 574, 375-386.
A.J. Bard, L.R. Faulkner. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, John Wiley: New York, 2001.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Analysis of the diffusion layer thickness, equivalent circuit and conductance behaviour for reversible electron transfer processes in linear sweep voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta. 2004, 49, 445-453.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Formulation and analysis of a simple analytical expression for irreversible electron transfer processes in linear sweep voltammetry and its experimental verification. Electrochim. Acta. 2004, 49, 2569-2579.
N.S. Nicholson, I. Shain. Theory of stationary electrode polarography. Single scan and cyclic methods applied to reversible, irreversible and kinetic systems. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 706-723.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Current function for irreversible electron transfer processes in linear sweep voltammetry for the reactions obeying Marcus kinetics. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 387, 317-321.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Evidence for the formation of radical anion in the reductive cleavage of carbon-bromine bond in 4′-Bromomethylbiphenyl-2-carbonitrile. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 414, 55-60.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Cleavage of an aromatic carbon–heteroatom bond in a single step or successive steps?––A mechanistic distinction in the reduction of 5-bromo-1,3-dichloro-2-iodobenzene. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 4741-4744.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Electrochemical reductive cleavage of carbon–halogen bonds in 5-bromo-1,3-dichloro-2-iodobenzene. Tetrahedron. 2004, 60, 10967-10972.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Distinction between stepwise and concerted mechanisms in reductive cleavage reactions—use of voltammetric current function in the analysis of non-linear kinetic laws. Tetrahedron. 2005, 61, 1785-1791.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Electrochemical reductive cleavage of carbon-chlorine bond in 1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene. Electrochim. Acta. 2005, 51, 242-246.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Solvent effect on the electrochemical reductive cleavage of carbon tetrachloride – A novel example of the deviation from the quadratic activation-driving force relationship. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 390, 261-267.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Electrochemical reductive cleavage of carbon tetrachloride in aqueous – nonaqueous binary solvents. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 569, 127-134.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Hammett-type relationship for the cleavage of radical anions of aromatic chlorides and bromides. Tetrahedron. 2005, 61, 3755-3758.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Linear kinetic and free energy correlations for intra molecular dissociative electron transfers – Estimation of standard potentials and cleavage rate constants of radical anions of aromatic halides. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 421, 193-197.
M. Arun Prasad, M.V. Sangaranarayanan. Estimation of the Gibbs free energy of transfer of electrolytes from aqueous to organic solvents – A novel application of the quadratic activation-driving force relationship. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003 382, 325-331.
ISSN 2347 – 8853
Indexed in:
 ISSN 2347 – 8853
ISSN 2347 – 8853  Â
Â