Review of computational approaches to model transcranial direct current stimulations tDCS and its effectiveness
Abstract
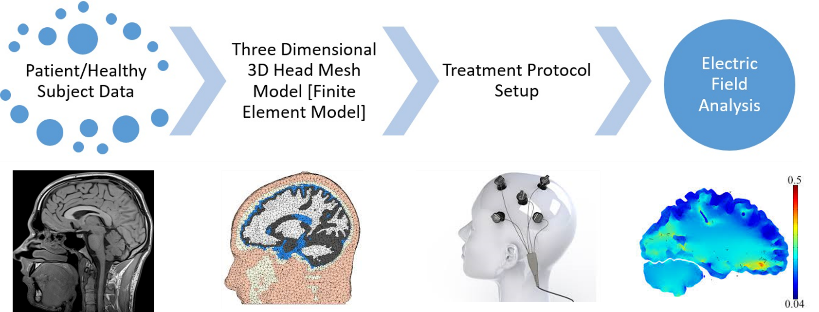
Neurological and psychological disorders are being treated by health professionals using medical technologies including drug therapy, electrical stimulation, and psychotherapy in some cases. Because of side effects caused by required drugs and social stigma for psychotherapy, these techniques have some limitations for their applicability in Mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Huntington disease (HD), dementia, major depressive disorder (MDD) and related neurological abnormalities.  Transcranial direct current stimulation is a non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) technique that uses small currents to alter characteristics of a healthy and diseased neuron. Even though sophisticated tDCS devices are being used for treatment, treatment protocol and its efficacy is still a debatable question. Researchers have found ways to model tDCS computationally to know the outcome of treatment. This review provides details of computational approaches used to model tDCS. We have reviewed clinical and computational practices carried out by researchers to model treatment modality for tDCS.Â
 ISSN 2321-4635
ISSN 2321-4635