Open Access

Subscription Access
Assessing the antimycobacterial activity of the bioactive fractions of the Indian medicinal plant - Justicia adhatoda L.
Smita Mishra, Manisha Khatri, Varsha Mehra
Abstract
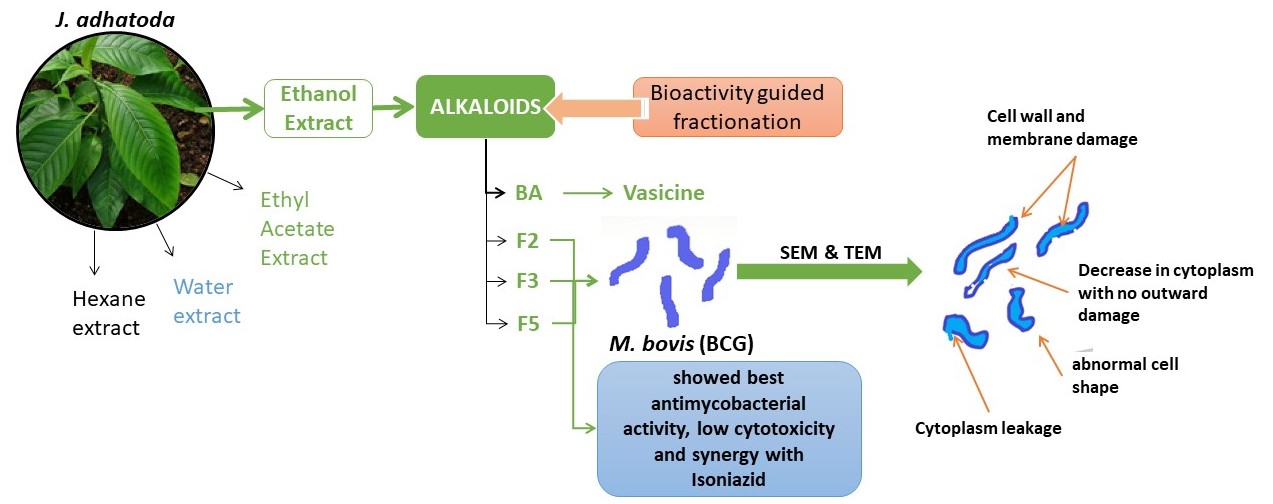
Justicia adhatoda is an Indian medicinal plant used largely to treat respiratory ailments, especially in Ayurvedic medicine. In the present study, we sought to analyze the antimycobacterial activity of the leaf extracts of J. adhatoda. The leaves of J. adhatoda were powdered and extracted with ethanol, water, ethyl acetate, and hexane and antimycobacterial activity was assessed by MABA. The ethanol extract showed >96% and 98% reduction in CFU at 100μg/ml on Mycobacterium smegmatis and Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) respectively. Active phytoconstituent from ethanol extract was isolated and further fractionated via Prep-TLC. The isolated fractions showed strong anti-mycobacterial activity, with low cytotoxicity and synergism when used with isoniazid. When subjected to electron microscopy, the fractions were found to adversely affect the cell wall and membrane of BCG, causing cytoplasmic leakage. Our study demonstrates that the active fractions isolated from J. adhatoda could be evaluated further for potentially effective anti-mycobacterial bioactive phytoconstituent.
Keywords
Tuberculosis; Natural products; Ayurveda; Bioactive constituents
Full Text:
PDF

ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825