Open Access

Subscription Access
Nitazoxanide/Camostat combination for COVID-19: An unexplored potential therapy
Manisha Khatri, Payal Mago
Abstract
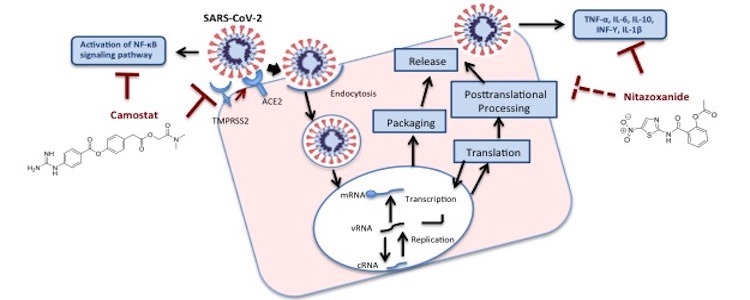
Novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) lies behind the ongoing outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and its ripple effects has brought major challenges to worldwide health systems. Urgent strategies are required to manage this pandemic and repurposing of existing drugs offer an option forward. A combination drug therapy for COVID-19 aims to prevent both the virus entry/spread as well as quelling the immune system havocs that the virus wreaks in the human body. This article analyzes Nitazoxanide/Camostat combination for their potential activity against SARS-CoV-2. Nitazoxanide, FDA approved drug potentiates host antiviral response, thereby reducing viral replication, titer and ensuing immune dysregulation. Camostat, a potent serine protease inhibitor blocks viral cell entry along with the potential to decrease COVID-19-associated hypercoagulability. Both the drugs do not inhibit cyp P450 enzymes and could be co-administered. Based on the combined pathophysiological and pharmacological potential, the drugs combination potentially recommended for early evaluation and clinical trials of this combination.
Keywords
COVID-19; Nitazoxanide; Camostat; Hypercoagulability; SARS-CoV-2.
Full Text:
PDF

ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825