Open Access

Subscription Access
Obesity, systemic inflammation and male infertility
Koushik Bhattacharya, Pallav Sengupta, Sulagna Dutta, Ivan Rolland Karkada
Abstract
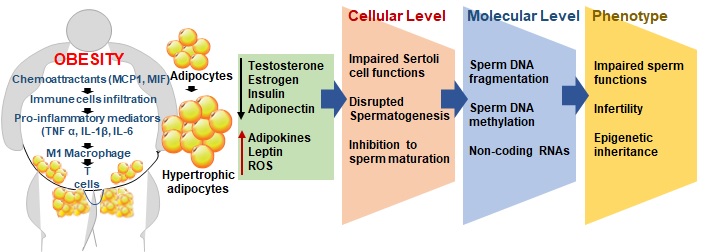
Obesity has turned global epidemic serving as a common cause from which various health problems are emerging. The induction of an obesogenic environment and its associated pathophysiology is complex. Studies in the last few decades have explained the role of different factors in the induction of obesity and related complications, such as obesity-induced male infertility. Among these factors, the endocrine and inflammatory factors are the major contributors that lead to male reproductive issues in obese men. However, the exact mechanism by which obesity-induced systemic inflammation or endocrine disruption may affect testicular functions or semen parameters remains elusive.  The obesogenic physiological environment drives immune responses towards TH-1 cells-dominated chronic inflammatory process, which adversely affects all the major organs including the testes, epididymis, and male accessory glands. The pro-inflammatory mediators including the cytokines interfere with the intricate reproductive regulations by the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal/testes (HPG/HPT) axis and thereby affect testicular functions. Most prominently, impaired steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis lead to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and poor semen parameters. Moreover, the inflammatory responses may stimulate the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) establishing testicular oxidative stress (OS), which in turn may cause hormonal haywire as well as direct damage to the spermatozoa including sperm membrane damage, mitochondrial and nuclear DNA fragmentation and epigenetic modifications. This article aims to review the updated literature and depict a concise concept on the association of obesity and male infertility through the incurrence of systemic inflammatory processes. This may encourage the conduction of further interdisciplinary research to recognize and strategize potential therapeutic approaches to deal with obesity-related male fertility problems.
Keywords
cytokines; obesity; inflammation; male infertility; semen quality
Full Text:
PDF

ISSN 2347–9825
Authors/visitors are advised to use Firefox browser for better experience of journal site.
Open Access: Researcher from developing/low economy countries can access the jorunal contents through WHO-HINARI .
 ISSN 2347-9825
ISSN 2347-9825